
It is obvious, then, that the number of protons in a nucleus (or, the nuclear charge, or the atomic number) determines the chemical properties of an element. The number of electrons in an atom, in turn, is determined by the nuclear charge. The reason is that an element's chemical properties depend on the number and arrangement of electrons in its atoms. When atomic number, rather than atomic mass, is used to construct a periodic table, these problems disappear. Certain pairs of elements (tellurium and iodine constitute one example) appear to be misplaced when arranged according to their masses. Although he was essentially correct, the periodic table constructed on this basis had three major flaws. Mendeleev had said that the properties of the elements vary in a regular, predictable pattern when the elements are arranged according to their atomic masses. Moseley's discovery made possible a new understanding of the periodic law first proposed by Dmitri Mendeleev in the late 1850s. Moseley hypothesized that the regular change in wavelength from element to element was caused by an increase in the positive charge on atomic nuclei in going from one element to the next heavier element. He discovered that the wavelength of the reflected x rays decreases in a regular predictable pattern with increasing atomic mass. an atom is zero in a neutral substance that contains atoms of only one element. present at the top right corner (right superscript) of an atomic symbol represents the charge on the atom of that element when it is in its ionic form. Moseley bombarded a number of chemical elements with x rays and observed the pattern formed by the reflected rays. By definition, the oxidation number of an atom is the charge that atom. Group 2 elements are alkaline Earth Metals with a. The concept of atomic number evolved from the historic research of Henry Gwyn-Jeffreys Moseley in the 1910s. Group 1 elements are the alkali metals that have a charge of +1. In nuclear chemistry, an element's atomic number is written to the left and below the element's symbol since an element's atomic number can always be determined simply by knowing its symbol, however, the former is often omitted from a nuclear symbol, as in 16O, where the superscript represents the atomic mass. It is always the smaller whole number found in association with an element's symbol in the table. So, elemental nickel, iodine, and gold have ZERO net charges.The atomic number of an element can be read directly from any periodic table. Some of the ions of the given elements are $N,etc$. Non-metals (to the right of the Periodic Table) gain electrons to form anions, while metals lose electrons to make cations. To be sure, elements can form ions when electrons are lost or gained. Atoms that lose electrons acquire a positive charge as a result because they are left with fewer negatively charged electrons to balance the positive charges of. Every positive charge has an equal and opposite negative charge.

It is a thick, soft, malleable, and ductile metal that is bright, somewhat reddish yellow in its pure form.Īs we know, matter is electrically neutral. At ordinary conditions, it exists as a glossy, purplish-black non-metallic solid, which melts to produce a deep violet liquid at 114 degrees Celsius and boils to produce a violet gas at 184 degrees Celsius.Īu - Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au (from Latin: aurum) and an atomic number of 79, making it one of the higher atomic number elements found in nature. I – Iodine is a chemical element with atomic number 53 and the symbol I. Ions are formed by the transfer of electrons. Nickel is a transition metal that is both hard and ductile. For elements in groups 6 and 7, the charge on the ion is equal to (8 minus group number). It's a glossy silvery-white metal with a faint golden hue. Ni - Nickel is a chemical element with the atomic number 28 and the symbol Ni.
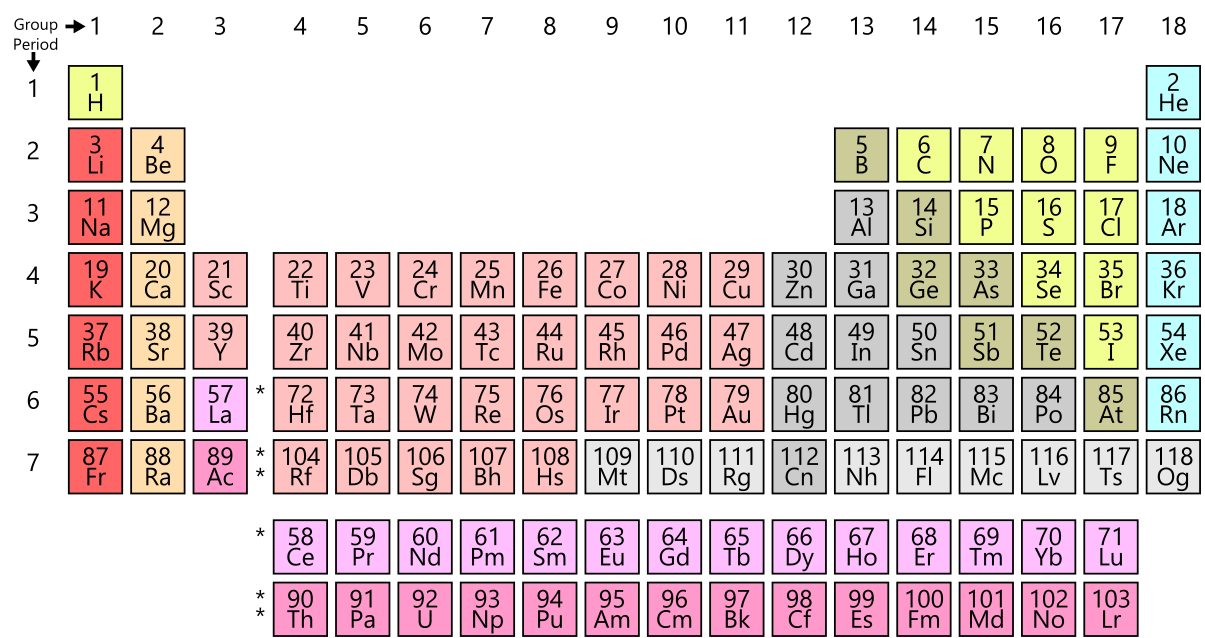
The object is electrically neutral if the number of protons and electrons is equal. The net charge on an object is negative if there are more electrons than protons. Net charge: When there are more protons than electrons in an object, the net charge is positive. Metals are on the table's left side, while nonmetals are on the right. The periodic table is a tabular arrangement of chemical elements that is ordered by increasing atomic number and grouping elements by repeating qualities. Hint : To answer this question, we first need to understand what a periodic table is.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
